 |
| AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbook Solutions PDF: Download Andhra Pradesh Board STD 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Book Answers |
Andhra Pradesh Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbooks Solutions PDF
Andhra Pradesh State Board STD 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Books Solutions with Answers are prepared and published by the Andhra Pradesh Board Publishers. It is an autonomous organization to advise and assist qualitative improvements in school education. If you are in search of AP Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Books Answers Solutions, then you are in the right place. Here is a complete hub of Andhra Pradesh State Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life solutions that are available here for free PDF downloads to help students for their adequate preparation. You can find all the subjects of Andhra Pradesh Board STD 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbooks. These Andhra Pradesh State Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbooks Solutions English PDF will be helpful for effective education, and a maximum number of questions in exams are chosen from Andhra Pradesh Board.Andhra Pradesh State Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Books Solutions
| Board | AP Board |
| Materials | Textbook Solutions/Guide |
| Format | DOC/PDF |
| Class | 8th |
| Subject | Biology |
| Chapters | Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life |
| Provider | Hsslive |
How to download Andhra Pradesh Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbook Solutions Answers PDF Online?
- Visit our website - Hsslive
- Click on the Andhra Pradesh Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Answers.
- Look for your Andhra Pradesh Board STD 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbooks PDF.
- Now download or read the Andhra Pradesh Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbook Solutions for PDF Free.
AP Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbooks Solutions with Answer PDF Download
Find below the list of all AP Board Class 8th Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbook Solutions for PDF’s for you to download and prepare for the upcoming exams:8th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Who discovered the cell for the first time?
Answer:
It was the year 1665 Robert Hooke, a British scientist observed thin slices of cork under a simple magnifying device which he had made himself. He observed that the cork resembled the structure of a honey comb consisting of many empty spaces or empty box like structures. He thought it was made up of very small cavities, Robert Hooke called these cavities “Cell”.
Question 2.
Name the factors on which shape of the cells depend.
Answer:
The shape and size of the cells vary considerably but all of these cells ultimately determined by the specific function of the cells.
e.g.: Amoeba is changing its shape for specific functions like collection of food and locomotion.
The shape of the cell may vary for giving definite structure to the organism, e.g,: Epidermal cells.
Question 3.
Distinguish between unicellular and multi cellular organisms.
Answer:
| Unicellular | Multicellular |
| 1) An organism composed of just one cell. | 1) An organism composed of more than cell. |
| 2) Many of nature’s simplest creatures called “unicellular organisms”. | 2) More biologically advanced creatures, called “multicellular organisms”. |
| 3) Cell is an individual form no gathering to perform tasks, but they live together. | 3) Different kinds of cells are joined together to perform specialized tasks. |
| 4) The single cell a unicellular organism possesses, the smaller its body, e.g.: Amoeba, Chlamydomonas. | 4) The more cells a multicellular organism possesses, the larger its body, e.g.: Fish, Neem tree. |
Question 4.
How will you prepare slide without drying quickly?
Answer:
Preparation of slide is a technique to observe microscopic structures. Microscopic slide is prepared on a 2 mm thick. Thin flat plant material directly placed in a drop of water on the glass slide. A drop of glycerin is added to the water to keep the material for longer time. Glycerine saves the material from drying quickly.
Question 5.
Deekshith said that, “we can’t see cells with unaided eye.” Is the statement true or false? Explain.
Answer:
We can’t see cell with naked eye is true. All living things formed by microscopic cells which are visible through microscope only but the egg of birds is visible without microscope. The size of the cells in living organism may be as small as the millionth of a meter.
Most of the cells either in unicellular and multicellular are small in size to perform all the life processes perfectly. The smallest cell 0.1 to 0.5 micrometers found in bacteria. Some of the cells can be seen with naked eye. The largest cell 17 cm x 18 cm egg of Ostrich.
Question 6.
Correct the statement and if necessary rewrite. (OR)
What is cell wall and what are its functions?
a) Cell wall is essential in plant cells.
b) Nucleus controls cell activity.
c) Unicellular organisms perform all life processes like respiration, excretion, growth and reproduction.
d) To observe nucleus and organelles clearly, staining is not necessary.
Answer:
a) Cell wall is essential in plant cells.
Plant cell walls are essential for plant life and also have numerous industrial applications, ranging from wood to nutraceuticals.
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, in addition to acting as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell wall is found in plants, bacteria, fungi, algae, archaea. Animals and protozoa do not have cell walls. “Plant cell wall is an essential component of biotic stress response mechanisms.”
b) Nucleus controls cell activity.
By containing the instructions for protein products in the DNA of the nucleus. All “control” work in the cell is carried out by proteins, such as enzymes, though DNA codes for other structural material, only protein has metabolic and behavioural control in the organism’s cells. Thus, the nucleus is the cell’s control center.
c) Unicellular organism perform all life processes like respiration, excretion, growth and reproduction.
All living organisms perform some basic life processes like respiration, excretion, etc., to sustain its life and improve its race. Unicellular organisms also perform all life processes.
d) To observe nucleus and organelles clearly, staining is not necessary.
To observe nucleus and organelles clearly, staining is necessary. Staining is a technique to get attached color to different parts of a cell. This helps to highlight particular areas in the cell.
Question 7.
Describe the structure of Nucleus.
Answer:
The nucleus is the largest cellular organelle in animals. In mammalian cells, the average diameter of the nucleus is approximately 6 micrometers (pm), which occupies about 10% of the total cell volume.
Question 8.
Explain the functions of Nucleus.
Answer:
Functions:
- The main function of the cell nucleus is to control gene expression and mediate the replication of DNA during the cell cycle.
- The nucleus provides a site for genetic transcription that is segregated from the location of translation in the cytoplasm, allowing levels of gene regulation that are not available to prokaryotes.
Question 9.
What is difference between cells in onion peel and cells in Spinach?
Answer:
Cells in onion peel arranged systematically with prominent nucleus. Cells in spinach are in different sizes and shapes without nucleus to perform nutrition.
Question 10.
Label parts of diagrammes given below. And identify which one is plant cell and which one is animal cell.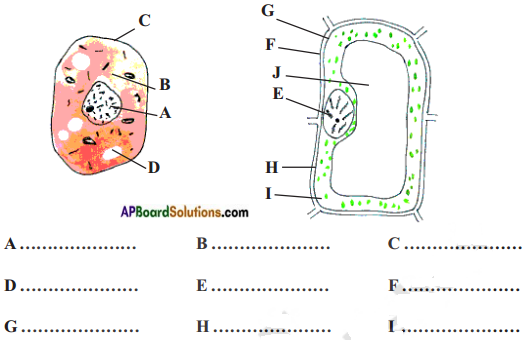
Answer:
A. Nucleus
B. Cytoplasm
C. Cell membrane
D. Vacuole
E. Nucleus
F. Cell wall
G. Cell membrane
H. Vocuole
I. Vacuole
Question 11.
What questions will you pose to know diversity in cells?
Answer:
- Are all the cells similar in shape and size?
- Do you find nuclei in all the cells?
- How many different types of cells could you see?
- What are the different shapes of the cells?
- Do all the cells one of the same in length?
Question 12.
If you want to know about unicellular and multicellular organisms, what questions will you pose?
Answer:
- What do you mean by unicelluar organism?
- What do you mean by multicellular organism?
- Give examples for unicellular and multicellular organisms.
- What are the differences between unicellular and multicellular organism?
Question 13.
Get some floating slime from a puddle, pick a very small amount of slime and put it on a slide. Separate out one fiber and look at it through the microscope. Draw the diagram what you have observed.
Answer: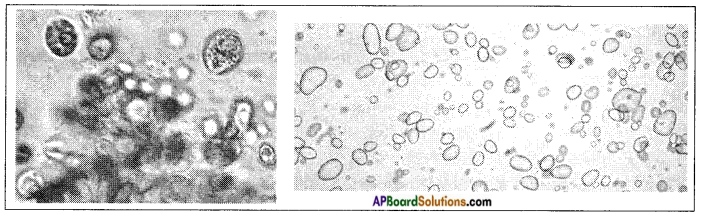
Question 14.
Collect different kinds of leaves from your surroundings and observe the shapes of the epidermal cells under microscope. Make a table which contains serial number, name of the leaf, shape of the leaf, shape of the epidermal cells. Do not forget to write specific findings below the table.
Answer: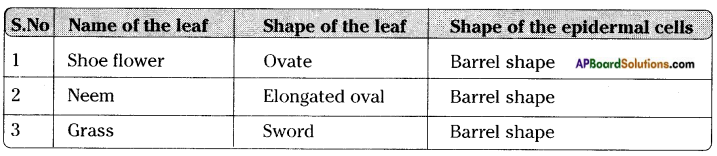
Question 15.
Make sketches of animal and plant cells which you observed under microscope.
Answer: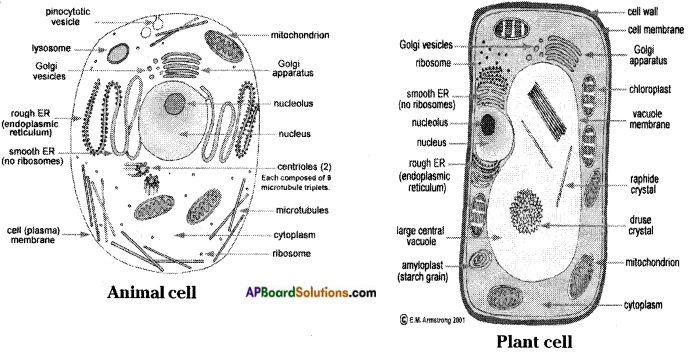
Question 16.
Ameer said “Bigger onion has larger cells when compared to the cells of smaller onions”! Do you agree with his statement or not? Explain why.
Answer:
The sizes of the cells in living organisms are too small to be seen with naked eye. The size of the cell is related to its function. The cell has to perform similar function in all living organisms.
The size of the onion depends upon the number of cells and not the size of the cell. Cells are of different shape, size and number.
Hence, I don’t agree with Ameer. “Bigger onions have larger cells when compared to the cells of smaller onions”.
Question 17.
How do you appreciate the fact that a huge elephant, man and trees are made of cells, which are very small and we can look at them through microscope?
Answer:
The size of the cells in living organisms may be as small as the millionth of a meter (micron) or may be as large as a few centimeters. Majority of the cells are too small to be seen with naked eye.
The size of the cell is related to its function. For example, nerve cell both in man and animals are long and branched. They perform the same functions that of transferring message.
The size of the organism is depending upon the number of cells and not the size of the cell. Cells are of different shape, size and number.
Question 18.
Deepak said, “A plant can’t stand erect without cell wall”. Support this statement.
Answer:
Deepak said, “A plant can’t stand erect without cell wall.” We support this statement with the following reasons.
i) Plant cells differ from those of animals in having an additional layer around the cell membrane.
ii) We called if as ‘cell wall’.
iii) Cell wall gives strength and rigidity to planks.
So a plant can’t stand erect without cell wall.
8th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Cell: The Basic Unit of Life InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Make different questions to know cells and cell organelles.
Answer:
- What are the structures present in the cells?
- Why cells are considered to be structural and functional unit of life?
- What is the need of cell wall in plant cells?
- Did we see the cells with naked eye?
Question 2.
Prepare different questions to know the discovery of cell.
Answer:
- In which year cell discovered?
- Name the scientist who observed cells.
- What type techniques used to observe the cell?
- Is there any special devices used to study the cell?
- Name the different devices used for discovery of cell.
- Can we see living cells under the microscope?
Question 3.
Prepare permanent slides of Onion cell, cheek cell and compare practically.
Answer:
Take inner layer of onion and cheek cells. Stain them with saffranin or methylene blue and keep coverslip.
Observe both the slides under microscope. Cell membrane and cell wall is present in both the cells. Dark stained nucleus is presented in the centre of the cell.
Comparison between onion and cheek cells:
| Onion cells | Cheek cells |
| Cells arranged compactly | Cells arranged loosely |
| Boundary of onion is cell membrane | Boundary of cheek cell is cell wall |
| Cytoplasm and nucleus is present | Cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus |
| Cell organelles present in cytoplasm | Cell organelles present in cytoplasm. |
Question 4.
Explain diversity in leaf cells practically.
Answer:
Take a section of Neem leaf on the slide and put a drop of water, cover it with a coverslip and observe it under the microscope. We can see different types of tissues present in the leaf. The section of leaf shows the following features.
Three groups of tissues arranged in leaf.
The first group epidermis where the cells are barrel shaped and covered by waxy material for protection.
The second group mesophyll tissue where the cells contain chloroplasts for nutrition. Cells arranged loosely with air spaces and stomata for exchange of gases.
The third group vascular tissue where the cells are thick walled to transport water and food.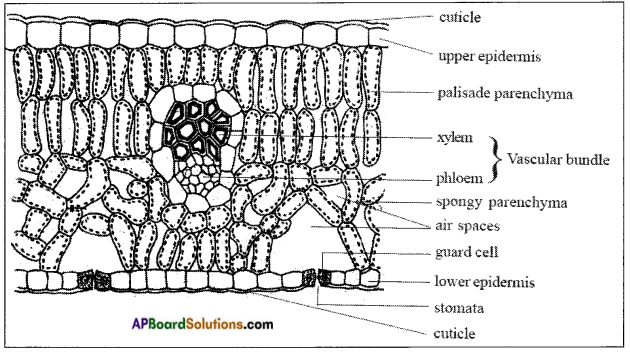
Question 5.
Make a sketch of blood cells.
Answer: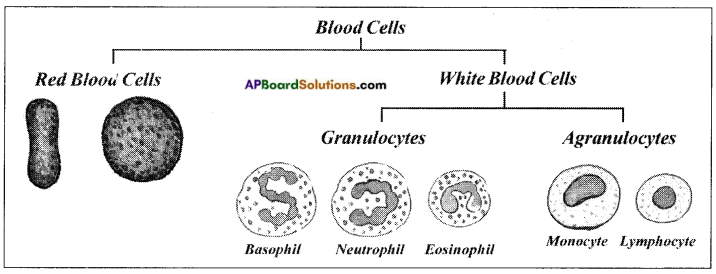
Question 6.
Draw a neat diagram of Clilamydomonas.
Answer: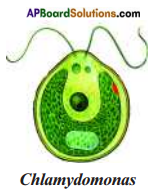
Question 7.
Make a sketch of Amoeba. (OR)
a) Draw a labelled diagram of Amoeba.
b) What are pseudopodia?
Answer:
a)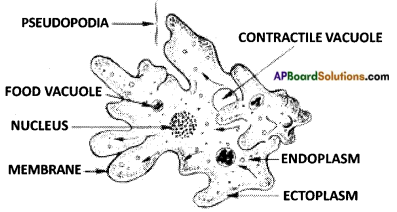
b) The projections on the body of amoeba which help in locomotion and collecting food.
Question 8.
Have you listened to the words of the cell? Guess how big a cell is? Is the number and sizes of cells in both man and elephant the same? Are the cells of an elephant bigger than that of a man?
Answer:
The size of the cells in living organisms may be as small as the millionth of a meter (micron) or may be as large as a few centimeters. Majority of the cells are too small to be seen with naked eye.
The size of the cell is related to its function. For example, nerve cell in both man and elephant are long and branched. They perform the same functions that of transferring message.
The size of the organism is depending upon the number of cells and not the size of the cell. Cells are of different shape, size and number. Hence size of cells in both elephant and man are same. The number of cells are more in elephant than man.
8th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Activities
Activity – 2
Question 1.
Prepare a slide of an onion peel and find out the special characters.
Answer:
Peel an onion and cut out a small fleshy portion from the bulb. Break this into two small parts and try to separate them. We notice a thin film like material holding the pieces together. Take out small portion and spread it evenly on a slide. Cover it with a cover slip and observe it under microscope.
Draw the figure what you have observed.
Cells are arranged side by side without any gaps.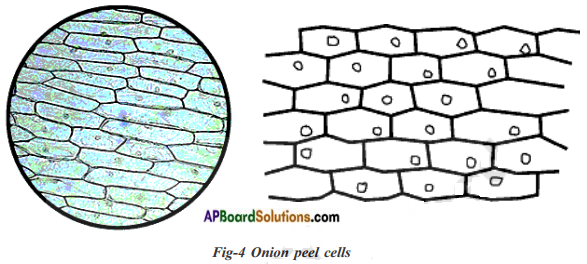
Activity – 4
Question 2.
Observation of the Nucleus in onion peel cells. (OR)
Sahitya is trying to observe the nucleus in the cells of onion peel. Explain the procedure to be followed for the experiment.
Answer:
Peel a membrane an onion now keep this membrane on a slide and add 1-2 drops of the stain (saffranin, methylene blue or red ink). Cover this with a cover slip and leave it for about five minutes. Then add water drop-wise from one side of the cover slip while soaking the extra water with a filter paper from the other side. This will help in washing away the extra stain. Now observe this slide under a microscope. The blue spot observed within the cell is the nucleus.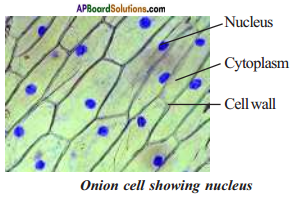
Activity – 5
Question 3.
Observe the following pictures and answer the questions given below.
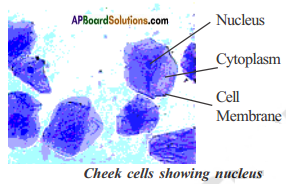
i) What are the structures present in the cells ?
Answer:
Cell wall in onion cell and cell membrane in cheek cell.
Cytoplasm and nucleus are common in both the cells.
ii) Did you see a tiny dark stained thing in all the cells ?
Answer:
Yes there is a tiny dark stained nucleus is common in both the cells.
iii) Are they located in the center of the cell in both the cells ?
Answer:
Nucleus located in center of both the cells.
iv) What is the difference between boundary of onion cell and cheek cell ?
Answer:
Cell wall is the boundary of onion and cell membrane is the boundary of cheek cell.
Activity – 6
Question 4.
Collect leaves stems and roots of different plants from the field and take sections to study different types of cells and tissues present in leaf and stems practically.
Answer:
Take a section of grass leaf on the slide and put a drop of water, cover it with a cover slip and observe it under the microscope. We can see different types of tissues present in the leaf.
The section of root or stem shows the following features.
Four groups of cells can be observed.
First group is outermost layer called epidermis.
It protects stem or root externally.
Major portion of stem or root has second group of cells.
This group synthesizes food and preserve food.
Third group of cells transport water and food.
Fourth group of cells placed centrally.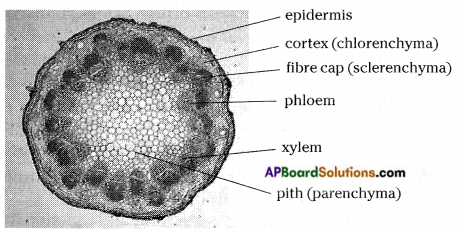
Question 5.
a) Observe the following cells and collect permanent slides.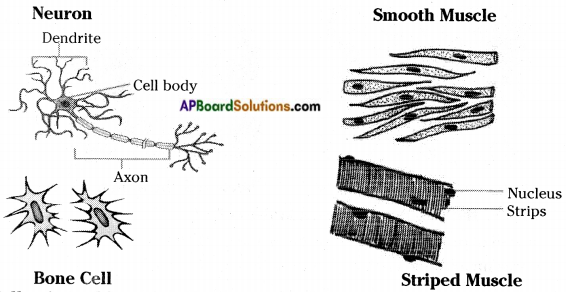
b) Fill the following table with help of your teacher.
| Name of the cell | Shape of the cell | Name of the parts observed in it |
| RBC | Biconcave | Blood tissue |
| Smooth Muscle Cell | Rod | Muscles |
| Nerve Cell | Tree | Brain, spinal cord and nerves |
| Bone Cell | Star | All bones |
| White Blood cell | Amoeboid | Blood tissue |
i) Are there any similarities in shape of the cells?
Answer:
No similarity is found in the shape and size of the above cells.
ii) Do you find nuclei in all the cells?
Answer:
In human RBC nucleus is absent. Muscle, Nerve, Bone and White Blood Cells consist nucleus.
iii) Do you know, which cell is the longest in all animals?
Answer:
Nerve cell is the longest in all animals
AP Board Textbook Solutions PDF for Class 8th Biology
- AP Board Class 8 Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 1 What is Science Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Basic Unit of Life Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 3 Story of Microorganisms 1 Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 3 Story of Microorganisms 2 Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 4 Reproduction in Animals Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 5 Attaining the Age of Adolescence Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 6 Biodiversity and its Conservation Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 7 Different Ecosystems Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 8 Production and Management of Food From Plants Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 9 Production and Management of Food From Animals Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 10 Not For Drinking-Not For Breathing Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology Chapter 11 Why Do We Fall Ill Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 1st Lesson విజ్ఞానశాస్త్రం అంటే ఏమిటి? Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 2nd Lesson కణం – జీవుల మౌళిక ప్రమాణం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 3rd Lesson సూక్ష్మజీవుల ప్రపంచం 1 Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 3rd Lesson సూక్ష్మజీవుల ప్రపంచం 2 Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 4th Lesson జంతువులలో ప్రత్యుత్పత్తి Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 5th Lesson కౌమార దశ Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 6th Lesson జీవ వైవిధ్యం – సంరక్షణ Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 7th Lesson వివిధ ఆవరణ వ్యవస్థలు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 8th Lesson మొక్కల నుండి ఆహారోత్పత్తి Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 9th Lesson జంతువుల నుండి ఆహారోత్పత్తి Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 10th Lesson పీల్చలేము – తాగలేము Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 8 Biology 11th Lesson మనకు అనారోగ్యం ఎందుకు కలుగుతుంది? Textbook Solutions PDF






0 Comments:
Post a Comment