 |
| इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1 मराठी स्वाध्याय PDF |
या लेखात, आम्ही नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1 विषयासाठी इयत्ता सातवी मराठी सोल्यूशन्स देऊ. इयत्ता सातवी मधील विद्यार्थी पाठ्यपुस्तकांमध्ये उपस्थित असलेल्या व्यायामांसाठी प्रश्न आणि उत्तरे डाउनलोड आणि कॉपी करण्यास सक्षम असतील.
इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1ाच्या पुस्तकात महाराष्ट्र बोर्डाच्या अभ्यासक्रमातील सर्व प्रश्नांचा समावेश आहे. येथे सर्व प्रश्न पूर्ण स्पष्टीकरणासह सोडवले आहेत आणि डाउनलोड करण्यासाठी विनामूल्य उपलब्ध आहेत. महाराष्ट्र बोर्ड इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1ाचे पुस्तक खाली दिले आहे. आम्हाला आशा आहे की आमच्या इयत्ता सातवी वीच्या नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1ाचे पुस्तक तुमच्या अभ्यासात मदत करेल! जर तुम्हाला आमचे इयत्ता सातवी चे पुस्तक आवडले असेल तर कृपया ही पोस्ट शेअर करा.
इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1 स्वाध्याय
|
मंडळाचे नाव |
Maharashtra Board |
|
ग्रेडचे नाव |
सातवी |
|
विषय |
नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1 |
|
वर्ष |
2022 |
|
स्वरूप |
PDF/DOC |
|
प्रदाता |
|
|
अधिकृत संकेतस्थळ |
mahahsscboard.in |
समाधानासह महाराष्ट्र बोर्ड आठवा स्वाध्याय कसे डाउनलोड करायचे?
महाराष्ट्र बोर्ड सातवी स्वाध्याय PDF डाउनलोड करण्यासाठी खालील स्टेप्स फॉलो करा:
- वेबसाइट- Hsslive ला भेट द्या. 'स्वाध्याय' लिंकवर क्लिक करा.
- महा बोर्ड सातवी स्वाध्याय PDF पहा.
- आता महाराष्ट्र बोर्ड सातवी स्वाध्याय तपासा.
- डाउनलोड करा आणि भविष्यातील संदर्भांसाठी जतन करा.
इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1 स्वाध्याय उपाय
इयत्ता सातवी स्वाध्याय मधील विद्यार्थी खालील लिंक्सवरून नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1ाचे उपाय डाउनलोड करू शकतील.
Class 7 Civics Chapter 4 Fundamental Rights Part 1 Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Answer the following questions in brief:
Question 1.
What do you understand by ‘Fundamental Rights’?
Answer:
(i) Demanding one’s rights is insisting on creating an atmosphere conducive to the development of the self as well as the entire society.
(ii) The Indian Constitution has guaranteed equal rights to all citizens in order to create this conducive atmosphere.
(iii) These rights are Fundamental Rights.
Question 2.
Name the awards that are conferred by the Government upon people for their distinguished contribution in different fields.
Answer:
Padmashree, Padmabhushan, Padmavibhushan.
Question 3.
Why is it prohibited to employ children under 14 years of age in hazardous places?
Answer:
(i) Employing children under 14 years of age in hazardous places can be dangerous. Children may be grievously injured and they may even lose their life.
(ii) To prevent the exploitation of children and ban oppression of any kind, it is prohibited to employ children under 14 years of age in hazardous places.
Question 4.
Why has the Constitution given equal rights to all citizens?
Answer:
(i) We get rights at birth. Every newborn baby has a right to live.
(ii) The entire society and government takes efforts to ensure that the baby is in the best of health.
(iii) Only when all individuals get protection from injustice, exploitation, discrimination and deprivation, will they be able to develop their skills and qualities.
(iv) Demanding one’s rights is insisting on creating an atmosphere conducive to the development of the self as well as the entire society.
(v) The Indian Constitution has guaranteed equal rights to all citizens in order to create this conducive atmosphere.
2. Prepare a picture strip on the right to liberty
Answer: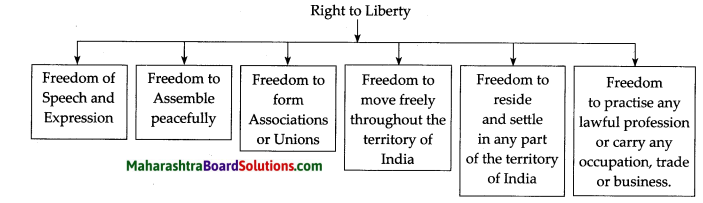
3. Correct and rewrite the following sentences:
Question 1.
No one gets rights at birth.
Answer:
We get rights at birth.
Question 2.
Government can deprive you of a job by discriminating on the basis of religion, sex, place of birth while giving government jobs.
Answer:
According to the Right to Equality mentioned in our Constitution the State cannot discriminate against any citizen on grounds of religion, sex, place of birth or other grounds
4. Complete the following graphical description.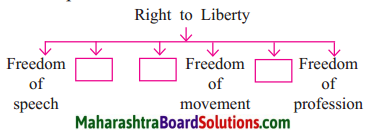
Answer:
Activities:
- Collect news clippings about certain important rights like the right to information, right to education, etc.
- If you find small children working on construction sites in your neighbourhood, talk to them and their parents about their problems and present the problems in your class.
Class 7 Civics Chapter 4 Fundamental Rights Part 1 InText Questions and Answers
Do this:
Following are the actions of A, B and C. Which kind of freedom do you connect them with?
Question 1.
‘A’ established ‘Adivasi Co-operation Forum’ to solve the problems of the tribal people.
Answer:
Freedom to Assemble Peacefully.
Question 2.
‘B’ decided to move his father’s bakery production from Goa to Maharashtra.
Answer:
Freedom to move freely throughout the territory of India.
Question 3.
‘C’ found some lacunae in the new tax policy of the Government. He wrote an artide about it and sent it to a newspaper for publication.
Answer:
Freedom of Speech and Expression.
Let’s discuss:
Question 1.
- Children are not employed here.
- Workers are paid daily here.
You see such boards in shops and hotels. In what way are they related to the Fundamental rights in the Constitution?
Answer:
They ensure that the Right against Exploitation mentioned in the Constitution is honoured and the right is not denied to the workers and children.
Question 2.
You must be aware of children’s rights. Can you name two important rights of children?
Answer:
(a) Right to Protection:
- Right to be protected from all sorts of violence.
- Right to be protected from physicaL and sexual abuse.
- Right to be protected from dangerous drugs.
(b) Right to Development
- Right to education
- Right to learn
- Right to relax and play
- Right to all forms of development – emotional, mental and physical.
Question 3.
Can rights be taken away?
Answer:
No, the rights cannot be taken away by anyone.
Question 4.
If rights are taken away, who should we contact for redressal?
Answer:
If rights are taken away one may appeal in the courts to seek justice for the same.
Question 5.
If the pet animals could speak, what rights do you think they would ask from you?
Answer:
- The right to roam around freely, wherever and whenever they wish.
- Right to expression
- Right to eat whatever they want whenever they want.
Question 6.
What are the advantages of equality before law and equal protection of the law?
Answer:
- There is no discrimination among citizens as superior – inferior, as men-women or while extending any protections like protection from arrest without a warrant.
- There is no discrimination among the citizens on the basis of religion, caste, race, sex, place of birth or residence.
- The inhuman practice of untouchability has been abolished in order to establish equality in the Indian society.
- Titles like Raja, Maharaja, Raobahadur etc. have also been abolished.
Class 7 Civics Chapter 4 Fundamental Rights Part 1 Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the sentence by choosing the appropriate words from the options given below:
Question 1.
The ______ has guaranteed equal rights to all citizens in order to create a conducive atmosphere.(Indian judiciary, Indian Government, Indian Constitution)
Answer:
Indian Constitution
Question 2.
We have protection from arrest without _______. (prior intimation, proof, warrant)
Answer:
warrant
Question 3.
________ gives a guarantee of all the liberties necessary from the point of view of an individual. (Right to Equality, Right to Liberty Right against Exploitation)
Answer:
Right to Liberty
Question 4.
______ implies getting a guarantee to live and availability of a conducive environment for living. (Right against Exploitation, Right to
Liberty, Right to Life)
Answer:
Right to Life
Question 5.
All children between 6 and ______ years of age are entitled to get education as a Fundamental Right. (11,10,14)
Answer:
14
Question 6.
It is prohibited to employ children under _______ years of age in hazardous places. (10,14,16)
Answer:
16
Match the following:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Right to Equality | (a) liberties necessary from the point of view of individuals |
| (2) Right to Liberty | (b) bans all types of oppression. |
| (3) Right against | (c) No discrimination |
| Exploitation | amongst citizens. |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – a
3 – b
Name the following:
Question 1.
The equal rights guaranteed to all citizens by the Indian Constitution in order to create a conducive atmosphere for the development of the self and the entire society.
Answer:
Fundamental Rights.
Question 2.
According to this right, the State cannot discriminate among citizens as superior- interior or men-women and cannot give different treatment or privileges to anybody.
Answer:
Right to Equality.
Question 3.
The State cannot discriminate against any citizen on these grounds for government employment.
Answer:
Religion, caste, race, sex, descent or place of birth or religion.
Question 4.
This inhuman practice that was prevalent in our country has been abolished by law.
Answer:
Untouchability.
Question 5.
These titles have been abolished as it creates artificial hierarchy among people.
Answer:
Raja, Maharaja, Raobahadur.
Question 6.
Any two freedoms we enjoy as Indian citizens.
Answer:
Freedom of Speech and Expression, Freedom to Assemble Peacefully.
Question 7.
The new right included in the Right to Liberty.
Answer:
Right to Education.
Question 8.
Children between this age group are entitled to get education as a Fundamental Right.
Answer:
6-14 years.
Question 9.
Two places where children cannot be made to work.
Answer:
Factories, Mines.
Question 10.
It implies getting a guarantee to live and availability of a conducive environment for living.
Answer:
Right to Life.
Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
When will individual be able to develop their skills and qualities?
Answer:
Only when all individuals get protection from injustice, exploitation, discrimination and deprivation, will the individuals be able to j develop their skills and qualities.
Question 2.
What does demanding one’s rights imply?
Answer:
Demanding one’s rights is insisting on creating an atmosphere conducive to the development of the self as well as the entire society.
Question 3.
What does the Right to Education ensure?
Answer: Right to Education ensures that no child between the age of 6 and 14 will be deprived of education.
Question 4.
Which are the different forms of exploitation which are prevented through Right against Exploitation?
Answer:
Bonded labour or forcing somebody to work against his wish, treating somebody like a slave, denying them legitimate compensation, making them do excessive or strenuous work, starving them or ill-treating them are different forms of exploitation which are prevented through Right against Exploitation
Write short notes on:
Question 1.
Right to Equality
Answer:
According to the Right to Equality, the State cannot discriminate among citizens as superior-inferior or a men-women and cannot give different treatment or privileges to anybody. The same law applies equally to all. Many laws give protection. For example, we have protection from arrest without warrant. The State cannot discriminate even while extending such protection.
Question 2.
Right to Liberty
Answer:
This is a very important right given by the Constitution. It gives a guarantee of all the liberties necessary from the point of view of the individual. As Indian citizens, we have the right to:
- Freedom of speech and expression.
- Freedom to assemble peacefully.
- Freedom to form associations or unions.
- Freedom to move freely throughout the territory of India.
- Freedom to reside and settle in any part of the territory of India.
- Freedom to practise any profession, or to carry on any occupation, trade or business.
Question 3.
Right against Exploitation
Answer:
(i) The right against exploitation implies the right to prevent exploitation.
(ii) While the Constitution has banned all types of oppressions through the right against exploitation, it has made a special provision to prevent the exploitation of children.
(iii) Accordingly, it is prohibited to employ children under 14 years of age in hazardous places.
(iv) Children cannot be employed or made to work in factories and mines.
(v) Exploitation includes bonded labour or forcing somebody to work against his wish, treating somebody like a slave, denying them legitimate compensation, making them do excessive or strenuous work, starving them or ill-treating them.
(vi) Generally women, children, the weaker sections of society and powerless people are exploited.
(vii) This right enables us to stand up against any kind of exploitation.
Correct and rewrite the following sentences:
Question 1.
No one gets rights at birth.
Answer:
We get rights at birth.
Question 2.
The government can deprive you of a job by discriminating on the basis of religion, sex, place of birth while giving government jobs.
Answer:
According to the Right to Equality mentioned in our Constitution the State cannot discriminate against any citizen on grounds of religion, sex, place of birth or other grounds.
Question 3.
People can have titles like Raja, Maharaja, Raobahadur etc.
Answer:
The Constitution has abolished titles like Raja,, Maharaja, Raobahadur etc., that create aq artificial hierarchy among people.
इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र स्वाध्याय उपाय
- इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र आमच्या राज्यघटनेचा परिचय मराठी स्वाध्याय PDF
- इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र संविधानाची प्रस्तावना मराठी स्वाध्याय PDF
- इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र संविधानाची वैशिष्ट्ये मराठी स्वाध्याय PDF
- इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 1 मराठी स्वाध्याय PDF
- इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र मूलभूत अधिकार भाग 2 मराठी स्वाध्याय PDF
- इयत्ता सातवी नागरिकशास्त्र राज्य धोरण आणि मूलभूत कर्तव्यांची निर्देशक तत्त्वे मराठी स्वाध्याय PDF







0 Comments:
Post a Comment