Andhra Pradesh Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbooks Solutions PDF
Andhra Pradesh State Board STD 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Books Solutions with Answers are prepared and published by the Andhra Pradesh Board Publishers. It is an autonomous organization to advise and assist qualitative improvements in school education. If you are in search of AP Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Books Answers Solutions, then you are in the right place. Here is a complete hub of Andhra Pradesh State Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century solutions that are available here for free PDF downloads to help students for their adequate preparation. You can find all the subjects of Andhra Pradesh Board STD 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbooks. These Andhra Pradesh State Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbooks Solutions English PDF will be helpful for effective education, and a maximum number of questions in exams are chosen from Andhra Pradesh Board.Andhra Pradesh State Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Books Solutions
| Board | AP Board |
| Materials | Textbook Solutions/Guide |
| Format | DOC/PDF |
| Class | 9th |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapters | Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century |
| Provider | Hsslive |
How to download Andhra Pradesh Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbook Solutions Answers PDF Online?
- Visit our website - Hsslive
- Click on the Andhra Pradesh Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Answers.
- Look for your Andhra Pradesh Board STD 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbooks PDF.
- Now download or read the Andhra Pradesh Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbook Solutions for PDF Free.
AP Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbooks Solutions with Answer PDF Download
Find below the list of all AP Board Class 9th Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbook Solutions for PDF’s for you to download and prepare for the upcoming exams:9th Class Social Studies 14th Lesson Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Choose the correct options.
a) Democraticand nationalist movements assumed that a nation has a ___________ ; (shared history; shared culture; shared economy; all the above; none of the abovd)
b) Jacobin clubs were established in different countries by ___________ (peasants; royalty; middle class; army)
c) During the mid 18th century the land was owned by ___________ and cultivated by ___________ (middle class, army, aristocrats, tenants)
Answer:
a) All the above
b) army
c) aristocrats, tenants.
Question 2.
After readingabout mid-eighteenth century Europe, what similarities or differences amongst people existed in the context of: language, ethnicity, trade practices.
Answer:
- Within the territories of the empire there lived diverse people.
- In the Alpine regions the aristocracy were predominently German – speaking.
- In Lombardy and Venetia people spoke Italy.
- In Galicia people spoke Polish.
- Bohemians, Slovaks, Slovens, Croats and Roumans were certain ethnic groups.
- The majority of the population was made up of the peasantry.
- Vast estates were there and they were cultivated by serfs.
- Trade and industry developed, commercial classesemergedduetothesedevelopments.
- A group of new middle class emerged due to the access to education and new ideas.
Question 3.
Do you agree with the statement: “when the emergence of nation states, the dominance of Aristocracy declined and middle class increased”. Give reasons.
Answer:
- Europe witnessed growth of industrial production and trade.
- This led to the growth of towns and the emergence of commercial classes whose existence was based on production for the markets.
- In its wake, new social groups came into being, (a working-class population and middle classes.)
- They had access to education and new ideas.
- It was among them that ideas of national unity and the abolition of aristocratic privileges gained popularity.
- There after the dominance of Aristocracy declined and middle class increased.
Question 4.
Write an imaginary dialogue between Mazzini and any of the Indian nationalist you have studied.
Answer:
Mazzini : We can’t form a nation state through talks, lectures, and discussions. We should do something.
Indian Nationalist : We can’t achieve freedom by revolutions and violent movements. We can’t achieve the unity of the nation. Time will decide it.
Mazzini : How long is this procrastination? We can achieve the unity through revolutionary organizations and secret fightings.
Indian Nationalist : It takes time for the people to get awareness. Nationality is strengthened when change comes in people.
Mazzine : We have to create the atmosphere of war. We should put an end to the monarchical and despotic rule.
Indian Nationalist : There is a way for that ………. We have to wait for some more time.
Mazzini : The situation will get worst if we still wait …………
Indian Nationalist : You know how French revolution was possible and what results it got.
Mazzini : The circumstances then were different.
Indian Nationalist : Agitations will not show solutions.
Mazzini : We have to decide soon. The flames of revolution should be lit in young people.
Question 5.
Mark sentences that describe conservatives and liberals. Try to identify examples in our contemporary context.
Answer:
| Conservatives | Liberals |
| 1. Conservatives are political philosophers who believe in preserving of traditional institutions like, church, monarchy etc. | 1. Liberals are political philosophers who believe in the freedom of the individuals. |
| 2. Conservatives stress on the strengthening of the autocratic monarchies. | 2. Liberals insist on a constitution and representative government through Parliament. |
| 3. They believe in the preserving of the privileges of the church. | 3. They stand for the end of privileges of the church. |
| 4. They believe in a dynamic economy with certain restrictions. | 4. They stand for the development of free trade and market and the abolishment of restrictions. |
| 5. Ex : Vatican City in Rome ruled by Pope. | 5. Ex: India. |
Question 6.
Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of France, Germany and Italy.
Answer:
| France | Germany | Italy |
| 1. Revolutionswereledby liberal nationalists especially middleclassesand commercial classes. | 1. Prussia, under the chief ministership of Bismark, took on the leadership for national unfication. | 1. Italian princely state of “Sardinia” took on the leadership. |
| 2. Reform Party leader “Theirs”, and socialist party leader “Louis Blanc” etc., are the leaders involved. | 2. Germany unification was a one man ship i.e., Otto von Bismarck with his policy “Blood and Iron” achieved the unification. | 2. Mazzini, a Philosopher, Gari-baldi, a sailor, Cavour, the chief minister and Victor Emmanuel II the ruler were involved in nation building process. |
| 3. People and leaders revolted against the kings and overthrown them. | 3. Bismark waged three wars, one with Denmark, second with Austria and finally with France, to achieve unification. | 3. There were five stages in the unification of Italy. The Southern states were united with the support of the local people. |
| 4. CharlesX was replaced by Louis Philippe in 1830. Louis Philippe was overthrown and a republic was established which was temporary. | 4. In January 1871, the Prussian king, William I, was proclaimed as German Emperor. | 4. Victor Emmanuel II was proclaimed king of united Italy. |
Question 7.
Explain what is meant by 1848 revolution of liberals. What were the political, social and economic ideas supported by the liberals?
Answer:
1848 revolt occurred duringthe period of Louis Philippe. Ideas of Socialism, Liberalism and Nationalism were increasing and finally resulted as Revolution of 1848. This revolution was led by liberal nationalists belonging to the educated middle-class and members of the commercial middle classes.
The ideas supported by the liberals were –
- All the parties opposed monarchy as the king grew more and more reactionary and conservative.
- Liberals raised their voice against the corruption of the government’s officials.
- Work to every citizen was the demand of the socialistic party.
- Reform Party leader ‘Theirs’ demanded extension of the suffrage and limitation of royal power.
Not finding any other alternative Louis Philippe abdicated the throne and fled away to England. In 1848, Liberals took control of France and abolished monarchy.
Question 8.
Briefly trace the process of Germany unification.
(OR)
Describe the unification of Germany.
Answer:
- Nationalist feeling wide spread among middle class Germans.
- They tried to unite the different regions of the Germany in 1848.
- But it was oppressed by the combined forces of the monarchy and the military.
- Later Prussia took on the leadership for national unification.
- Its Chief Minister Otto von Bismarck, was the architect of this process.
- He carried out this with the help of the Prussian army and bureaucracy.
- He waged three wars in seven years.
a) War with Denmark
b) Austro – Prussian war
c) Franco – Prussian war - Unification of Germany was accomplished by 1871.
- In January 1871, the Prussian king, William -1, was proclaimed German Emperor in a ceremony held at Versailles.
Question 9.
Locate some changes on Europe map drawn up by the Vienna Congress.
Answer: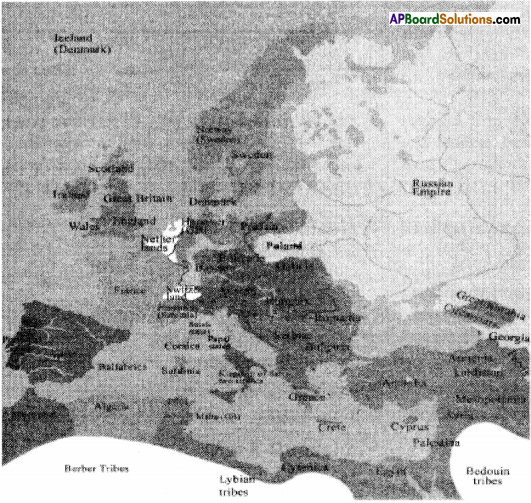
Question 10.
Read the last para of page 178 and comment on it.
| The 1830s were years of great economic hardship in Europe. The first half of the nineteenth century saw an enormous increase in population all over Europe. In most countries there were more seekers of jobs than employment. Population from rural areas migrated to the cities to live in overcrowded slums. Small producers in towns were often faced with stiff competition from imports of cheap machine-made goods from England, where industrialisation was more advanced than on the continent. This was especially so in textile production, which was carried out mainly in homes or small workshops and was only partly mechanised. In those regions of Europe where the aristocracy still enjoyed power, peasants struggled under the burden of feudal dues and obligations. |
Answer:
- Increasing economic hardship during the 1830s.
- Widespread unemployment, urban congestion, competition flow, machine made goods from England, Feudal dues, rising food prices, failed crops.
- Popular revolt in France in 1848 resulted in Louis Philippe fleeing, France declared a republic with voting for all men above – 21 and national workshops for more employment.
- Very critical conditions were prevailed.
Question 11.
Compare the map of Europe of mid 18th century (1815) with that of the present map of Europe and note down the changes you find, in a note book.
Answer: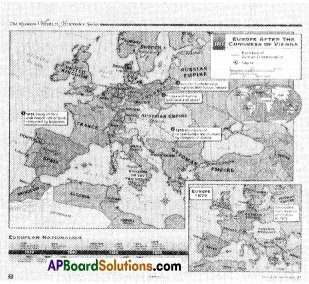
The Congress of Vienna was held in order to draw up a plan to alter Europe politically and territorially so as to prevent the extensive expansion of any one great power, such as that Napoleon had brought about. To main¬tain the balance of power and establish a old regimes and to pacify the situations Vienna congress divided the different regions of Europe were brought under the power of different strongholds of Europe.
Later on, when the nations like Italy and Germany took up the ideas of Nationalism and moved for unification, they defeated those powers, which were being ruled by the other European powers. As a result of this, the structure of Europe, established by the congress of Vienna, got redrawn, and the present day Europe is established.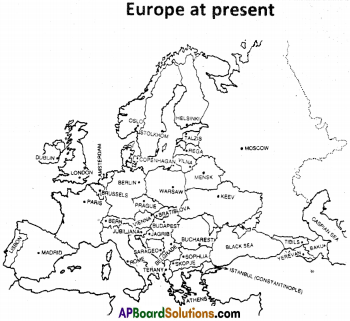
9th Class Social Studies 14th Lesson Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In what ways do you think Napoleon’s conquests would have helped in the emergence of nationalism in those countries? (Text Book Page No. 174)
Answer:
- Napoleon formed a new political union under French patronage and called it “confederation of the Rhine”.
- He had abolished 112 small states and merged them into a bigger nation.
- As a result the complicated political map of Germany was made easy.
- These confederations raised the feeling of the nationalism in those countries.
Question 2.
How did nationalism and the idea of the nation-state emerge? (Text Book Page No. 174)
Answer:
- A nation state was one in which the majority of its citizens came to develop a sense of common identity and shared common history.
- This commonness did not exist from time immemorial, it was forged through struggles, through the actions of leaders and the common man.
- The French revolution gave the term “nation” its modern meaning.
- A nation is not the territory but the people who make it.
- The French revolution gave the meaning of sovereignty that the people constituting the nation are the source of all power and authority.
- Government is answerable to its people.
All these ideals led to the formation of the nation -states.
Question 3.
Discuss the importance of language and popular traditions in the creation of national identity. (Text Book Page No. 174)
Answer:
- Language and popular traditions are important in the creation of national identity.
- National identity means people feeling that they belong to a nation irrespective of their caste, religion, colour etc.
- The language makes people identify themselves as a one race or a nation.
- Also the popular traditions such as Roman culture and tradition etc., easily attracted the people and strengthened the national integrity.
Question 4.
Explain why Charles X and Louis Philippe fled from france. (Text Book Page No. 180)
Answer:
- Revolutions means transformation of ideas and thoughts.
- Sometimes this transformations became violent and may lead to the execution of the king and queen.
Ex : Charles X and Louis X VI - In orderto avoid such kind of situations Charles X and Louis Philippe fled from France.
Question 5.
Describe the caricature. How does it represent the relationship between Bismarck and the elected deputies of parliament? What interpretation of democratic processes is the artist trying to convey? (Text Book Page No. 181)
Answer:
Bismarck’s dominance over the elected deputies of the Parliament is shown in the caricature. He followed ‘Blood and iron’ policy. He firmly believed that this policy only could achieve the unification of Germany but not the songs, speeches and festivals.
Question 6.
In what ways do you think the old kingdoms prevented the growth of trade and industry? (Text Book Page No. 176)
Answer:
- There was no free trade and there were lot of state-imposed restrictions.
- A merchant had to pass through so many customs barriers and pay a customs duty of about 5% at each customs officers.
- Due to these conditions, the growth of trade and industry was prevented in the old kingdom.
Question 7.
In what ways would liberal democracy have helped to develop trade and industry in those countries? (Text Book Page No. 176)
Answer:
- Liberal democracy stood for the freedom of markets.
- It also insisted on the abolition of state-imposed restrictions.
- Through the above measures, the liberal democracy have helped to develop trade and industry in their countries.
Question 8.
Do you think our country has a liberal democratic political system ? Give your reasons. (Text Book Page No. 176)
Answer:
- In India supreme power rests with the people.
- India is a republic country.
- Everyone is equal before law.
- Every citizen of 18 years and above has the right to vote.
- Any citizen is eligible to contest for any political office.
Hence we can say India has liberal democratic political system.
Question 9.
Why do you think conservatism needs to curb freedom to express ones opinion and criticise? (Text Book Page No. 176)
Answer:
- Conservatism is the dominance of society by an aristocracy. It is incompatible with democracy, prosperity and civilization in general.
- The conservatives did not tolerate criticism and dissent, and sought to curb activities that questioned the legitimacy of autocratic governments.
- They imposed censorship laws to control the ideas of liberty and freedom associated with the French Revolution.
Question 10.
What is the caricaturist trying to depict? (Text Book Page No. 177)
Answer:
The caricaturist is trying to depict the thoughts of Jacobin clubs and the discontentment among people on the freedom of speech.
Question 11.
Indian nationalists also sought to revive and give importance to folk arts in India. Why do you think they thought this was important?
Answer:
- Our Indian nationalists sought to revive and give importance to folk arts in India.
- This was done to carry the message to large audience who were mostly illiterate.
- Another reason to use folk art was to revive our ancient national spirit.
Question 10.
Do you think Italy became a true nation state with its unification under King Emmanuel II? Give your reasons.
Answer:
No, because the unification of Italy was only made territorially. The much of the Italian population was illiterate. They had no idea of nationalist ideology. The peasant masses in Southern Italy had never heard of Italia. Hence, we can say that Italy did not become a true nation state.
Question 11.
Hold a debate in the class between those who agree with conservatism and those who agree with liberal democracy on what is best for the welfare and development of people in Europe or in India.
Answer:
Conservatism means supporting monarchy. The conservatives wanted to protect traditional institutions of state and society like the monarchy, the church, social hierarchies, property and family. They supported the modernisation initiated by Napoleon.
In monarchy, the king is the final. It he is good administrator, the people under him will be benefited. Otherwise they will suffer a lot.
Liberal democracy means the representative of the people rules the country for the will and wish of the people only. Without the concern of the people, he may not have whole right to take any action. The people have the power to remove him from the power when he goes wrong. Hence the government itself is people’s. Thus, democracy is the best form of government.
AP Board Textbook Solutions PDF for Class 9th Biology
- AP Board Class 9 Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 1 Our Earth Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 2 The Natural Realms of the Earth Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 3 Hydrosphere Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 4 Atmosphere Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 5 Biosphere Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 6 Agriculture in India Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 7 Industries in India Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 8 Service Activities in India Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 9 Credit in the Financial System Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 10 Prices and Cost of Living Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 11 The Government Budget and Taxation Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 12 Changing Cultural Traditions in Europe 1300-1800 Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 13 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 17th and 18th Centuries Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 15 Industrialisation and Social Change Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 16 Social Protest Movements Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 17 Colonialism in Latin America Asia and Africa Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 18 Impact of Colonialism in India Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 19 Expansion of Democracy Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 20 Democracy An Evolving Idea Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 21 Human Rights and Fundamental Rights Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 22 Women Protection Acts Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 23 Disaster Management Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 24 Traffic Education Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 1 భూమి – మనం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 2 భూమి – ఆవరణములు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 3 జలావరణం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 4 వాతావరణం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 5 జీవావరణం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 6 భారతదేశంలో వ్యవసాయం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 7 భారతదేశంలో పరిశ్రమలు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 8 భారతదేశంలో సేవా కార్యకలాపాలు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 9 ద్రవ్య వ్యవస్థ – ఋణం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 10 ధరలు – జీవనవ్యయం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 11 ప్రభుత్వ బడ్జెట్ – పన్నులు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 12 యూరప్లో మారుతున్న సాంస్కృతిక సంప్రదాయాలు: 1300-1800 Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 13 17, 18వ శతాబ్దాలలో ప్రజాస్వామిక, జాతీయవాద విప్లవాలు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 14 19వ శతాబ్దంలో ప్రజాస్వామిక, జాతీయవాద విప్లవాలు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 15 పారిశ్రామికీకరణ, సామాజిక మార్పు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 16 సామాజిక నిరసనోద్యమాలు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 17 లాటిన్ అమెరికా, ఆసియా, ఆఫ్రికాలలో వలసవాదం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 18 భారతదేశంపై వలసవాద ప్రభావం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 19 విస్తరిస్తున్న ప్రజాస్వామ్యం Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 20 ప్రజాస్వామ్యం – రూపుదిద్దుకుంటున్న భావన Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 21 మానవహక్కులు, ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 22 మహిళా రక్షణ చట్టాలు Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 23 విపత్తుల నిర్వహణ Textbook Solutions PDF
- AP Board Class 9 Social Studies Chapter 24 రోడ్డు భద్రతా విద్య Textbook Solutions PDF







0 Comments:
Post a Comment